Infectious Coryza in chickens. And what to do about it.
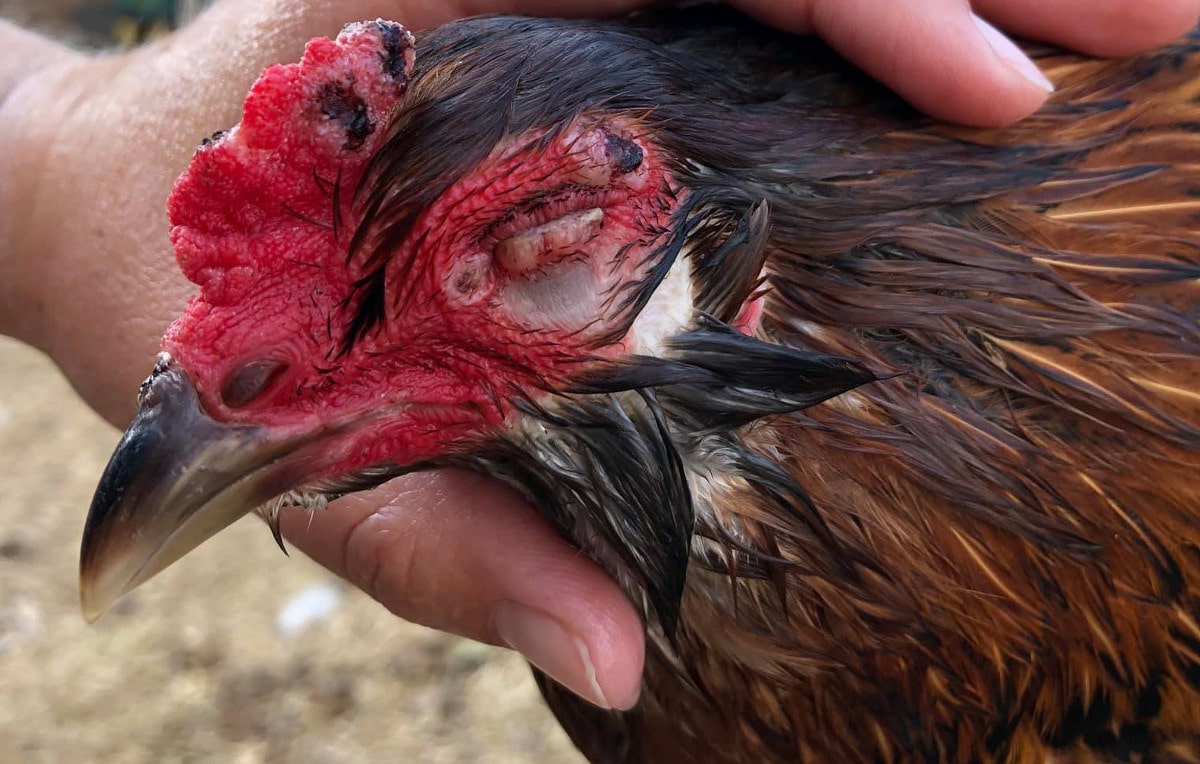
Infectious coryza is both painful and distressing for chickens. It is an acute respiratory disease of chickens characterised by nasal discharge, sneezing, and swelling of the face under the eyes.
Table of Contents
The bacteria which cause Infectious Coryza only infect chickens, not humans and is of no public health significance to the human population. The impact of the disease is purely economic in value.
Infectious Coryza or swollen head disease:
Infectious Coryza is a relatively common acute respiratory disease of chickens characterised by nasal discharge, sneezing, and swelling of the face under the eyes and is an intense respiratory infection.
Outbreaks usually result from the introduction of infected or carrier birds into a flock. The chicken can get this disease through contaminated water and contaminated surfaces. Similar bacteria cause infections in pheasants and guinea fowl.
Below: You can see how Infectious Coryza got it's alternative name of swollen head disease.

Infectious Coryza can be ingested or inhaled and is spread via contaminated feed or water or by the movement of chickens or poultry products from one flock to another or by the human keeper bringing the infection in.
Although infected birds grow more slowly and are more likely to be condemned as inedible the meat and eggs can still be consumed providing you take note of any withdrawal period for any medications the bird may be on.
Here are some key points about Infectious Coryza in chickens:
- Chickens of all ages can be affected even though it is more prevalent in the old or the young.
- Carrier birds, source of infection can be ingestion or inhalation and the incubation period is 24-48 hours.
- Chronic and healthy carrier birds remain carriers of infectious coryza for a long periods.
- Coryza occurs most frequently in fall and winter.
- Infectious Coryza is not an egg transmitted disease.
- Avibacterium paragallinarum is a sensitive bacteria form that is inactivated quickly outside the host.
- Infectious exudate suspended in tap water is inactivated in 4 hours at the surrounding temperature.
- When suspended in saline, the exudate is infectious for 24 hours at 22°C.
- Exudate or tissue stays infectious when held at 37°C for 24 hours and, now and again, if 48 hours at 4°C, exudate stays infectious for a few days.
- At temperatures of 45°C–55°C, Coryza is killed within 2–10 minutes.
The incubation period of infectious coryza is short, 24-48 hours after the inoculation of chickens with either culture or exudates symptoms begin to show and susceptible birds exposed by close contact to infected cases may show signs of disease within 24-72 hours.
The route of infection is conjunctival or nasal with an incubation period of 1-3 days followed by rapid onset of the disease over a 2-3 day period with the whole flock affected within 10 days. In the absence of any concurrent infections, Infectious coryza usually runs its course within 2-3 weeks.
It is not egg-transmitted and the bacterium survives 2-3 days outside the bird, but is easily killed by heat, drying and disinfectants.
The sign and symptoms of Infectious Coryza:
Chickens infected with Infectious Coryza may exhibit a range of clinical signs, including nasal discharge, sneezing, and coughing. Other symptoms can include facial swelling, swollen wattles, and a drop in egg production. Infected birds may also develop a foul-smelling discharge from their nostrils and have difficulty breathing.
Below: A classic case.
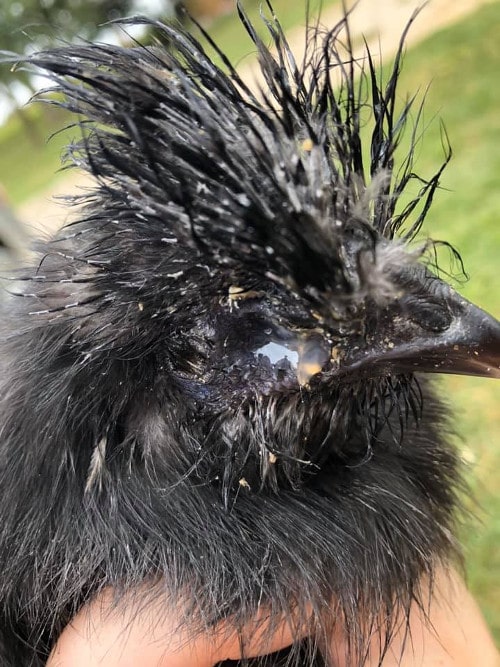

Coryzal signs and symptoms include:
- Acute inflammation of upper respiratory tract involvement of nasal passage and sinuses producing a smelly and sticky discharge from the eyes and nostrils.
- Facial oedema and conjunctivitis resulting in swollen face or eyes. Could be one or both. Their eyes will literally swell shut.
- Swollen head like syndrome are also been associated with Avibacterium paragallinarum are seen in broiler birds.
- Arthritis and septicaemia are seen in broiler and layer birds. Chickens may be immobile or move less and have a stiff gait.
- Decreased feed and water consumption in growing birds.
- Serous to mucoid nasal discharge.
- Swollen or discoloured comb or wattles may be evident especially in the male.
- In some outbreaks, peri-orbital swelling Conjunctivitis may be noticed.
- Difficulty in breathing. Rales, coughing, sneezing and snoring at night while perching.
- Diarrhoea and dirty vent feathers.
- Egg production may be delayed in young pullets and severely reduced in producing hens.
- A foul odour may be detected in the flock in which disease has been chronic and complicated by other bacteria.
Diagnosis in the flock is based on the history, clinical signs, and symptoms. A laboratory can isolate and identify the prescence of the organism directly.
The test involves taking exudate from sinuses after deep incision on the eye or from the trachea or air sac in the lungs.
There are no breed exceptions for this condition, the predisposing factors for Infectious Coryza are:
- Very young (1 to 3 weeks), very old, and stressed adult birds are more susceptible.
- Poor housing.
- Parasitism.
- Inadequate nutrition.
- Poor ventilation.
- Wet litter.
- Complication or co-infections with other conditions like Fowl pox, IB, ILT, Mycoplasma.
No location is safe from infection as Infectious Coryza is found worldwide but the disease is seen only in chickens although similar bacteria cause conditions in pheasants and guinea fowls.
In backyard flocks the disease seems to be more prevalent later in the chickens life and is particularly problematic in fall around moulting time when chickens are under stress already.
Chickens can and do survive Infectious Coryza and the prognosis is good with prompt treatment.
While the greatest economic loss related to Infectious Coryza results in poor egg production (marked reduction 10-40%) in layer and poor growth performance in growing chickens it can cause mortality especially in stressed or already weakened birds.
Reported moralities in commercial flocks is between 10% and 35% and as it is not a reportable disease figures are not available for backyard flocks. If there is co-infection with other conditions mortality may be as high as 50%.
Below: Sometimes it is not being able to see to eat that kills birds.
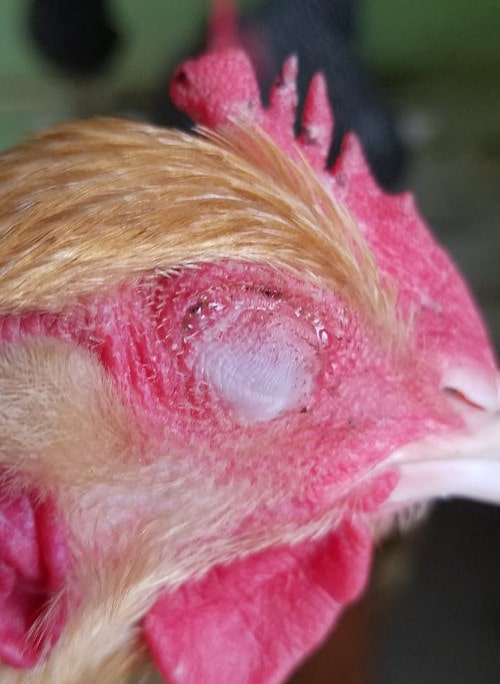
In my experience if it is caught quickly and treated properly mortality in backyard chickens is very low, I would expect 10% to 20% mortality with veterinary treatment.
The treatment of Infectious Coryza in chickens:
As Infectious Coryza is sensitive to certain antibiotics and the treatment is a prescribed antibiotic for 7 to 10 days.
It is important to remember that treatment will cure the acute infection but the chicken may go on to shed the bacteria from time time over the course of it's life and may relapse into an infected state requiring a second course of treatment.
It should be noticed that resistance against antibiotics in the Avibacterium paragallinarum happens. A multidrug-resistance plasmid has been accounted to be common in isolates of Avibacterium paragallinarum from Taiwan, with the plasmid providing resistance to streptomycin, sulfonamides, kanamycin, and neomycin.
Always remember to isolate sick birds from the rest to avoid spread of infections.
Treatment and duration depends on the severity of the initial infection. Treatment with antibiotics for 7 to 10 days as a flare-up may occur if treatment is too short or stopped prematurely.
In severe cases, culling of infected birds may be necessary to prevent the further spread of the disease, especially if it becomes widespread in a flock.
Other treatments are palliative, meaning they can relive the symptoms without curing the condition.
These include bathing the eyes in warm water and adding electrolytes the water to aid recovery. Your vet may have eye drops to help relive the symptoms and pain killers may be appropriate for backyard flocks. Warm and dry conditions will help as will softened feed.
Chickens take 3 weeks to recover from Infectious Coryza but without treatment the disease will infect a flock and run it's course within 30 to 40 days.
Treatment shortened the time taken by the chickens to recover and prevents some mortality.
There are no effective home or herbal remedies for Coryza. Colloidal silver is often touted as a remedy but it isn't considered safe or effective for any of the health claims. Silver has no known purpose in the body and not an essential mineral.
All home and herbal remedies can and should be given for palliative reasons to make the birds feel better and they may help with the chickens overall health but they won't cure the disease or speed recovery.
The prevention of Infectious Coryza:
Commercial vaccines for infectious coryza, typically based on killed H. paragallinarum, are widely available around the world. They are effective only against certain strains and only if the vaccination has taken place 30 days before infection.
You can take some measures to prevent infections:
- Biosecurity. Good biosecurity measures, proper sanitation, and vaccination can help prevent the disease.
- Carry out proper sanitation before new entry of chickens.
- Vacate coops, sheds and site for one month between flocks.
- Avoid practises such as purchasing breeding males or starting chicks from unknown sources.
- Only day-old chicks should be secured for replacement purposes unless the source is known to be free of Infectious Coryza.
- Isolation new from old stock.
- All-in / all-out system is the best way to avoid infectious coryza.
- Vaccination should be completed 4 weeks before infectious coryza usually breaks out on the individual farm.
- Controlled exposure to live organisms also has been used to immunize layers in endemic areas.
The bacteria which cause Infectious Coryza only infect chickens, not humans and is of no public health significance to the human population. The impact of the disease is purely economic in value.
