Air cells in eggs. Where to find them and what are they for.

All birds eggs have a hard shell made up of a protein matrix that has been mineralised, mostly with calcium carbonate. These shells have microscopic pores to allow for gaseous exchange or breathing.
The air cell or pocket is a small gap between the inner and outer membranes of the egg. It contains ordinary air with a very similar mix of gases to the atmosphere.
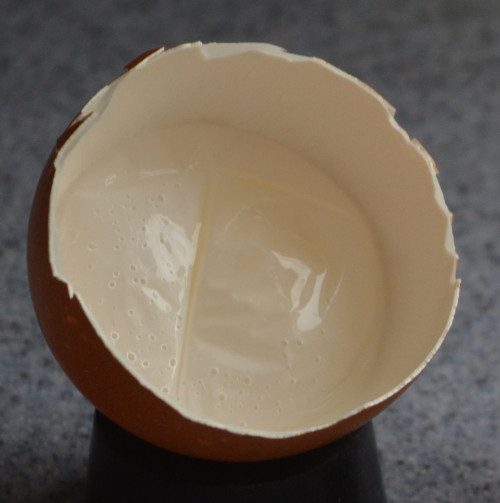
Below: This is the air cell as seen from inside the egg.

Air cells are found in all birds eggs and get larger as the egg gets older or the embryo develops.
Where is the air cell located in an egg?
The air cell is always located at the round end of the egg between the two membranes that separate the shell from the egg contents.
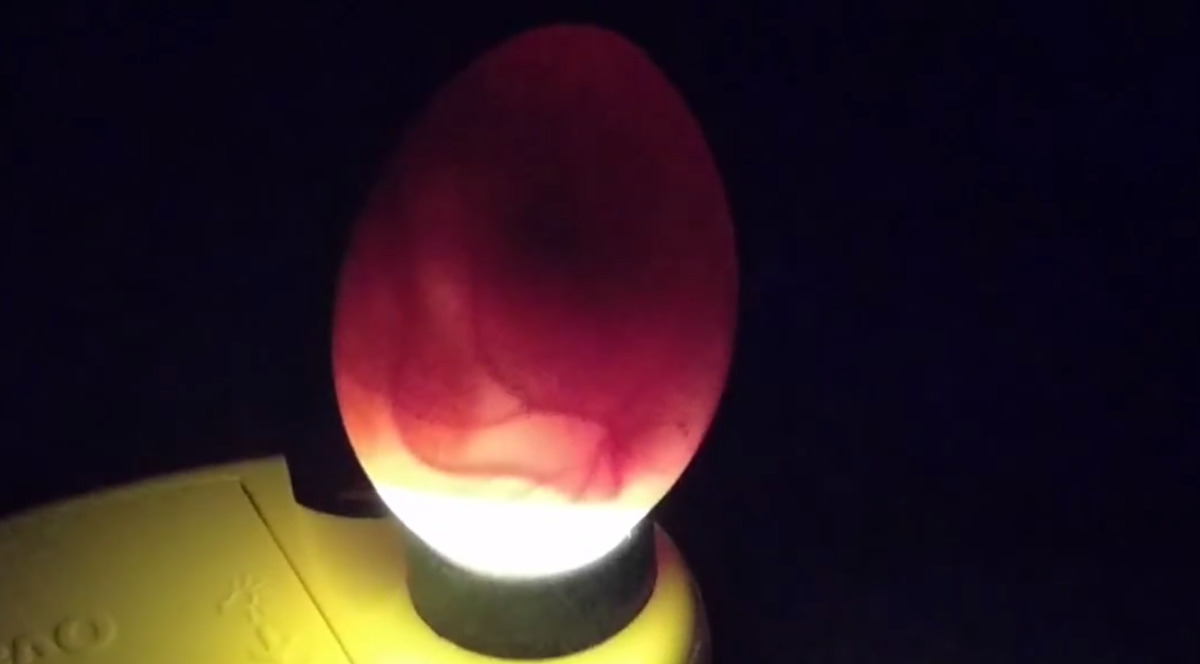
Below: The air cell should always be in the round or blunt end of the egg.
In this example above the air cell is the bright white section at the base of the egg.
An air space that moves around has become detached because the membranes have been damaged.
What is the function of air space in an egg?
The air cell or space in an egg has two functions:
- It allows for the inflation of the lungs after internal pipping in preparation for hatching.
- It provides the embryo with more room to position itself ready to hatch.
Gaseous exchange happens all over the surface of the egg, not just at the air cell site.
Below: The anatomy of the birds egg.
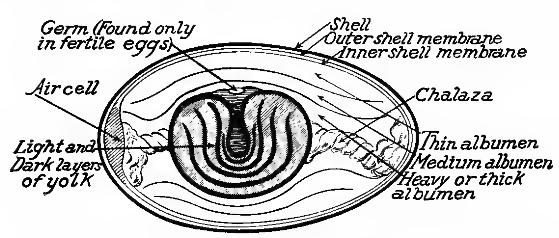
The proportion of carbon dioxide is slightly higher in the air cell as incubation progresses.
Do all eggs have air pockets?
All eggs develop an air cell or pocket as they cool after they have been laid. The air cells start of very small and grow in size as the egg develops or gets older.
Below: Me, showing the membranes that make up the air cell in an egg.
Video transcript: So this is the membranes that form the air cell. The first one is the internal one that encloses the egg white. There is another one that lines the inside of the shell.
How does air cell develop in egg?
There are more pores in the shell at the round end of the egg and this allows a tiny air space to form as the egg cools after being laid.
This air cell then grows in size as the eggs is incubated or dehydrates with age.
The size of the air space in an egg tells you how old the egg is. If it is very small the egg is fresh. The large the air cell becomes , the older the egg.
Below: An egg with a very large air sac. This egg has lost too much moisture during incubation.
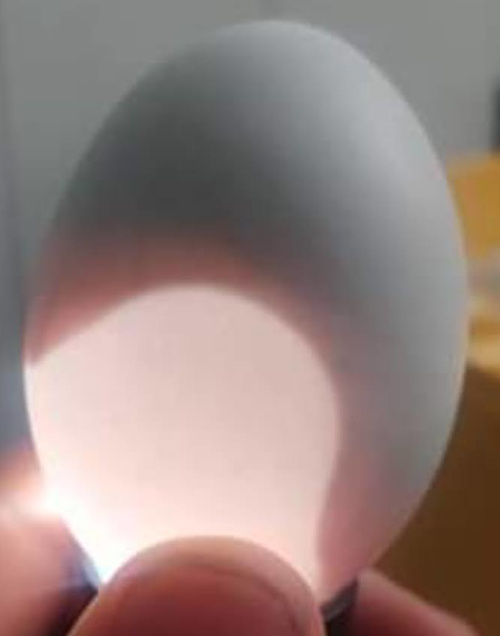

If the air cell is too small it means the humidity has been too high and there may not be enough air and space for the chick to hatch.
